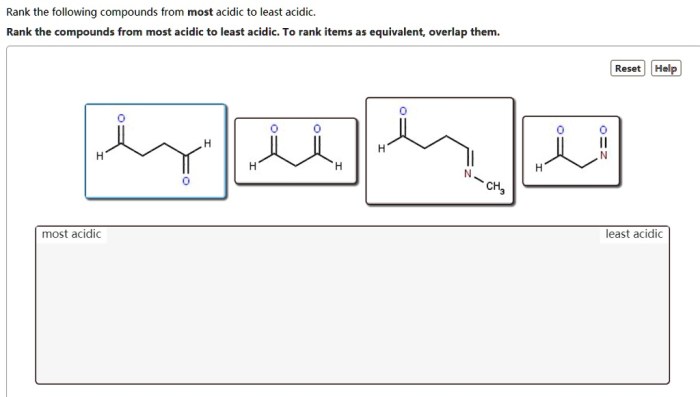
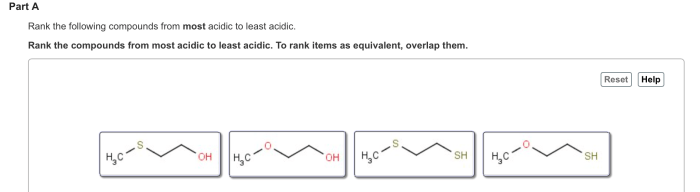
Rank the following compounds from most acidic to least acidic embarks on an enthralling exploration of the factors that govern the acidity of compounds. This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricacies of acidity constants, structural influences, solvent effects, and their profound impact on the chemical behavior of these substances.
Acidity, a fundamental property of compounds, plays a pivotal role in a vast array of chemical reactions and processes. Understanding the factors that modulate acidity is essential for unraveling the mechanisms underlying these phenomena and harnessing their potential in various scientific disciplines.
Acidity Constants
Acidity constants (Ka) are quantitative measures of the acidity of a compound. They represent the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of an acid in water, and are expressed as the negative logarithm of the equilibrium constant (pKa = -log Ka).
Ka values are used to determine the relative acidity of compounds. The lower the Ka value, the stronger the acid. This is because a lower Ka value indicates that the acid dissociates more readily in water, releasing more H+ ions and resulting in a lower pH.
Structural Factors Affecting Acidity
Electronegativity, Rank the following compounds from most acidic to least acidic
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. The more electronegative an atom, the more it will attract the electrons in a covalent bond, and the weaker the bond will be. In the case of acids, the electronegativity of the atom bonded to the hydrogen atom (usually oxygen or nitrogen) affects the acidity of the compound.
As electronegativity increases, the bond between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom becomes stronger. This makes it more difficult for the hydrogen atom to be released as a proton, and therefore the acid becomes weaker.
Resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when there are multiple possible Lewis structures for a molecule. In the case of acids, resonance can stabilize the conjugate base of the acid, making it less likely to protonate and therefore decreasing the acidity of the acid.
Hybridization
Hybridization refers to the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. The hybridization of the atom bonded to the hydrogen atom affects the acidity of the compound.
sp3-hybridized atoms are more acidic than sp2-hybridized atoms, which are in turn more acidic than sp-hybridized atoms. This is because the more s-character in the hybrid orbital, the more electronegative the atom becomes, and the stronger the bond between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom.
Solvent Effects
Solvent Polarity
The polarity of a solvent affects the acidity of a compound. Polar solvents, such as water, can stabilize the ions that are formed when an acid dissociates. This makes it more likely for the acid to dissociate, and therefore increases the acidity of the acid.
Nonpolar solvents, such as hexane, cannot stabilize the ions that are formed when an acid dissociates. This makes it less likely for the acid to dissociate, and therefore decreases the acidity of the acid.
Specific Solvent Effects
Some solvents can have specific effects on the acidity of certain compounds. For example, hydrogen bonding solvents, such as water, can form hydrogen bonds with the conjugate base of an acid, which can make the acid more acidic.
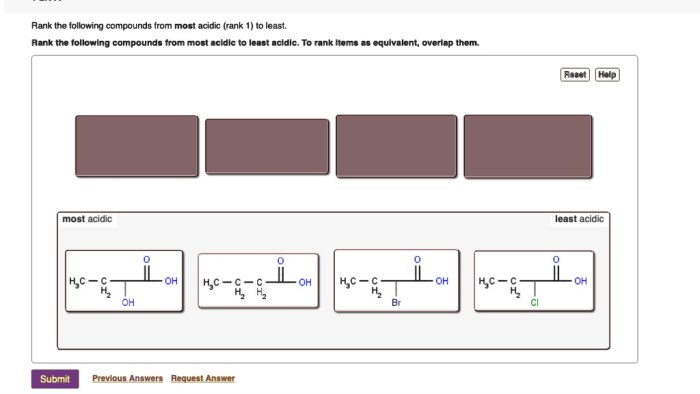
Ranking Compounds
| Compound | Formula | Ka | Acidity Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid | HCl | 1.0 x 10^-7 | 1 |
| Nitric acid | HNO3 | 2.1 x 10^-3 | 2 |
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 | 1.2 x 10^-2 | 3 |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH | 1.8 x 10^-5 | 4 |
| Water | H2O | 1.0 x 10^-14 | 5 |
Quick FAQs: Rank The Following Compounds From Most Acidic To Least Acidic
What is the significance of acidity constants in ranking compounds?
Acidity constants (Ka) serve as quantitative measures of the acidity of compounds. They provide a numerical scale that allows for direct comparison of the relative strengths of acids, enabling researchers to rank compounds based on their ability to donate protons.
How do structural factors influence the acidity of compounds?
Structural factors exert a profound influence on acidity. Electronegativity, resonance, and hybridization can significantly alter the stability of conjugate bases, thereby affecting the acidity of the corresponding compounds. Understanding these structural effects is crucial for predicting the acidity of complex molecules.
What role do solvents play in modulating acidity?
Solvents can have a significant impact on the acidity of compounds. Polar solvents, for instance, can stabilize charged species, leading to increased acidity. Conversely, nonpolar solvents tend to decrease acidity by reducing the solvation of ions. The choice of solvent is therefore an important consideration when studying acidity.