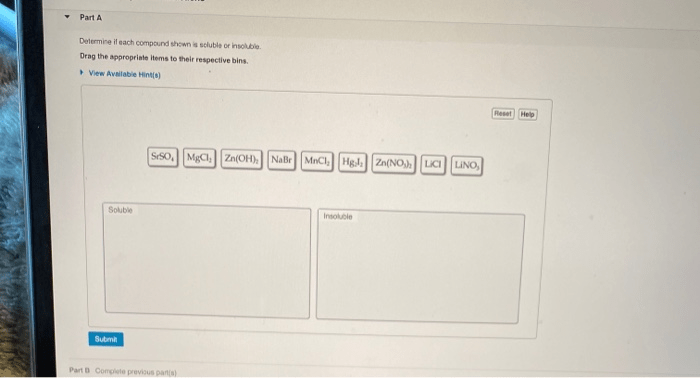
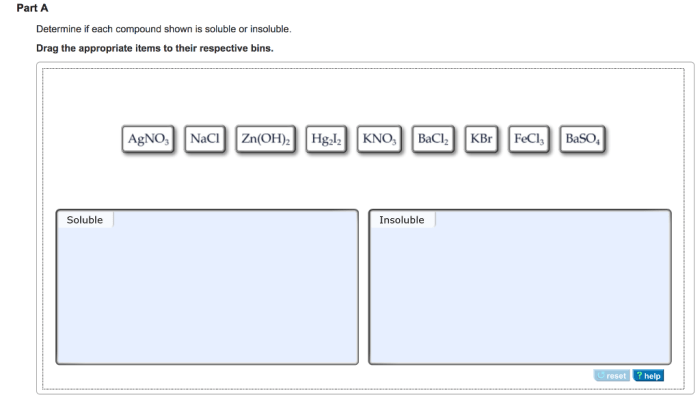
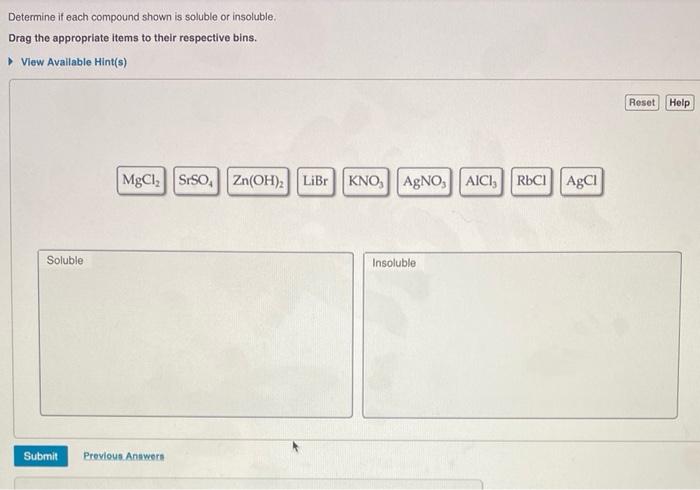
Determine if each compound shown is soluble or insoluble. – The solubility of chemical compounds plays a crucial role in various scientific and industrial applications. Understanding the factors that influence solubility is essential for predicting the behavior of compounds in different solvents. This article explores the concept of solubility, discusses the solubility rules for ionic and covalent compounds, and Artikels experimental methods for determining solubility.
It also highlights the practical applications of solubility in fields such as chemistry, pharmacy, and environmental science.
The solubility of a compound is its ability to dissolve in a given solvent. The extent of solubility is determined by the nature of the solute and solvent, as well as by factors such as temperature and pressure. In general, ionic compounds are more soluble in polar solvents, while covalent compounds are more soluble in nonpolar solvents.
However, there are exceptions to these rules, and some compounds exhibit solubility behavior that can be difficult to predict.
Compound Solubility Determination
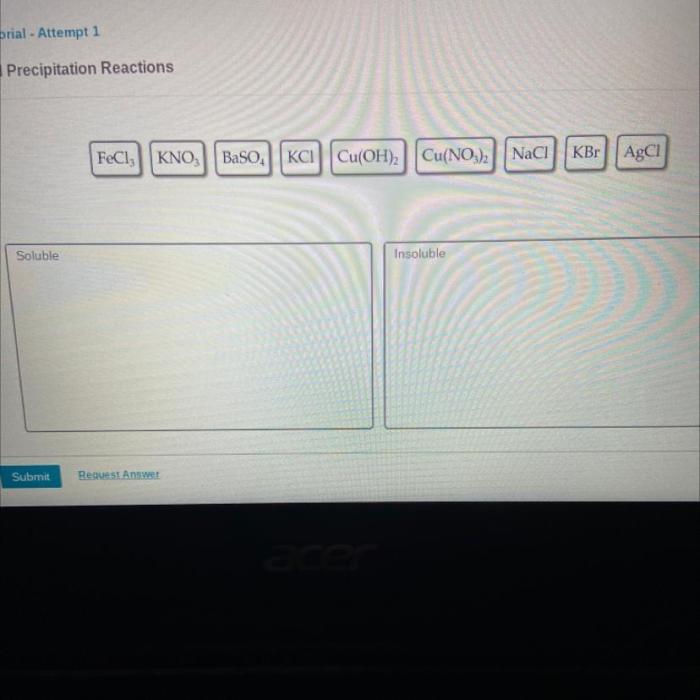
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, forming a homogeneous mixture. In the context of chemical compounds, solubility is influenced by various factors, including polarity, molecular weight, and temperature.
Polarity measures the uneven distribution of electrons within a molecule, and it affects solubility in polar solvents. Molecular weight, on the other hand, represents the mass of a molecule and can impact solubility based on the solvent’s ability to accommodate larger molecules.
Temperature plays a crucial role in solubility, with higher temperatures generally increasing the solubility of solids in liquids. However, the solubility of gases in liquids decreases with increasing temperature.
Solubility is significant in various chemical and industrial applications. It influences processes such as crystallization, drug delivery, and water treatment, among others.
Solubility Rules
For ionic compounds, predicting solubility based on cation and anion combinations is guided by solubility rules. These rules provide guidelines for determining whether an ionic compound is soluble or insoluble in water.
| Cation | Solubility | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+) | Soluble | None |
| Group 2 (Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+) | Soluble | Carbonates, phosphates, sulfates |
| NH4+ | Soluble | None |
| Ag+ | Insoluble | Nitrates, chlorides, bromides, iodides |
| Pb2+ | Insoluble | Nitrates, chlorides, bromides, iodides |
| Fe2+ | Insoluble | Nitrates, chlorides, bromides, iodides |
| Fe3+ | Insoluble | Nitrates, chlorides, bromides, iodides |
| Al3+ | Insoluble | Nitrates, chlorides, bromides, iodides |
| Anion | Solubility | Exceptions |
| Cl- | Soluble | Ag+, Pb2+, Hg2+ |
| Br- | Soluble | Ag+, Pb2+, Hg2+ |
| I- | Soluble | Ag+, Pb2+, Hg2+ |
| NO3- | Soluble | None |
| SO42- | Soluble | Ba2+, Sr2+, Ca2+ |
| CO32- | Insoluble | Group 1 cations |
| PO43- | Insoluble | Group 1 cations, Group 2 cations |
| OH- | Insoluble | Group 1 cations |
Exceptions to the solubility rules occur due to the formation of complex ions or the influence of other factors, such as pH and temperature.
Solubility of Covalent Compounds
Unlike ionic compounds, covalent compounds generally exhibit different solubility characteristics. Their solubility depends on factors such as polarity, hydrogen bonding, and molecular weight.
Polar covalent compounds, like alcohols and carboxylic acids, tend to be soluble in polar solvents like water. Nonpolar covalent compounds, such as hydrocarbons, are typically insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents like hexane.
Hydrogen bonding can significantly enhance the solubility of covalent compounds in water. For instance, ethanol is more soluble in water than butane due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Molecular weight also plays a role in solubility. Larger molecules with higher molecular weights tend to be less soluble in water compared to smaller molecules.
Experimental Determination of Solubility
The solubility of compounds can be determined experimentally using methods like gravimetric analysis and titrimetric methods.
Gravimetric analysis involves evaporating a known mass of the solution and measuring the mass of the solid residue. The solubility is then calculated based on the mass of the solid and the volume of the solution.
Titrimetric methods utilize a titrant of known concentration to react with the compound of interest. The solubility is determined by measuring the volume of titrant required to reach the equivalence point.
- Prepare a saturated solution of the compound in a solvent.
- Filter the solution to remove any undissolved solid.
- Measure the mass of a known volume of the saturated solution.
- Evaporate the solvent from the solution and measure the mass of the solid residue.
- Calculate the solubility using the formula: Solubility = (Mass of solid residue / Volume of solution) x 1000
Applications of Solubility, Determine if each compound shown is soluble or insoluble.
Solubility finds practical applications in various fields:
- Chemistry:Solubility is crucial in purification techniques like crystallization and fractional crystallization.
- Pharmacy:The solubility of drugs determines their bioavailability and effectiveness.
- Environmental science:Solubility influences the transport and fate of pollutants in the environment.
FAQ Resource: Determine If Each Compound Shown Is Soluble Or Insoluble.
What is the difference between solubility and insolubility?
Solubility refers to the ability of a compound to dissolve in a solvent, while insolubility refers to the inability of a compound to dissolve in a solvent.
What factors affect the solubility of a compound?
The solubility of a compound is affected by factors such as the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure.
How can I determine the solubility of a compound?
The solubility of a compound can be determined experimentally using methods such as gravimetric analysis and titrimetric methods.