Draw 2 2 dimethylbutane show all hydrogen atoms – Delving into the realm of organic chemistry, we embark on an exploration of 2,2-dimethylbutane, a captivating hydrocarbon that showcases a unique arrangement of carbon and hydrogen atoms. This discourse delves into the molecular intricacies of this compound, unraveling its structural characteristics, chemical properties, and the profound influence of its hydrogen atoms.
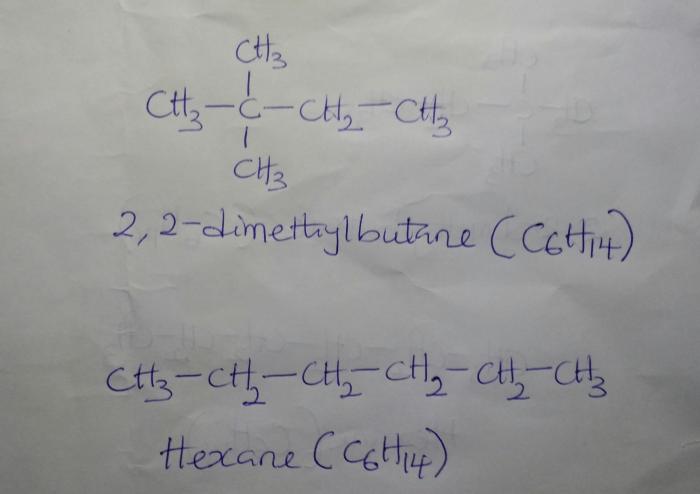
2,2-Dimethylbutane, an isomer of pentane, possesses a captivating molecular architecture. Its central carbon atom forms the backbone, adorned with four additional carbon atoms and ten hydrogen atoms. The two methyl groups, each bonded to one of the central carbon’s terminal carbons, impart a distinctive branched structure to the molecule.
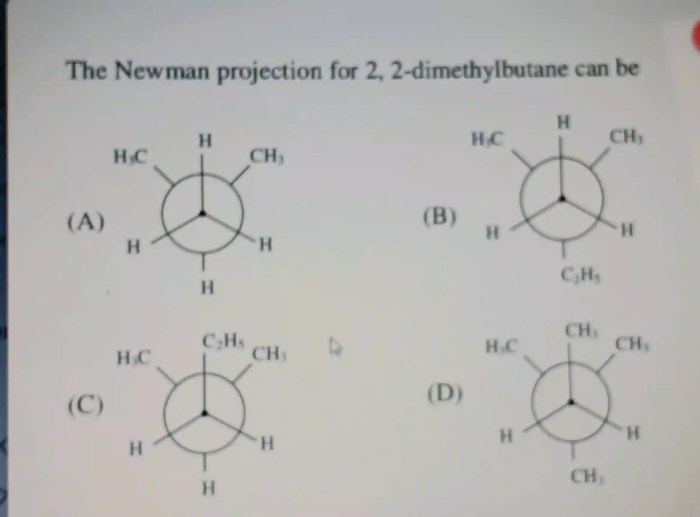
2,2-Dimethylbutane: Structural Overview and Hydrogen Atoms
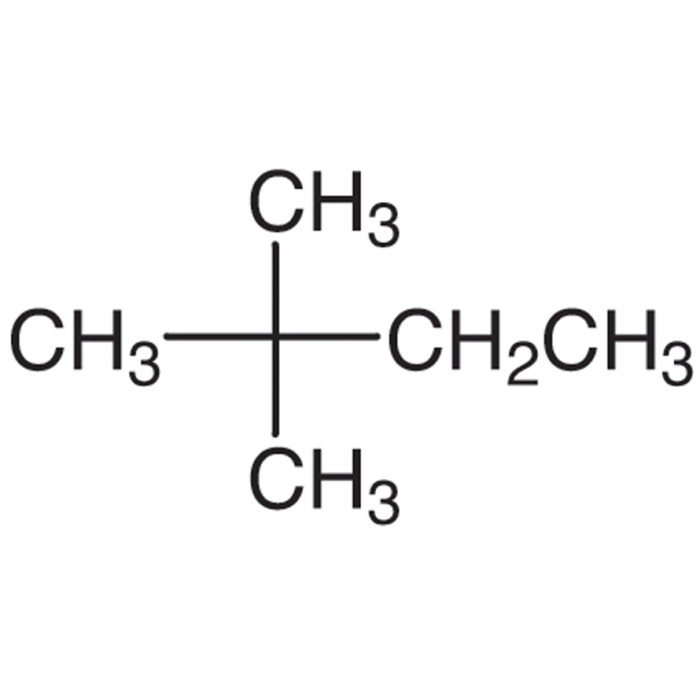
,2-dimethylbutane is an alkane with the molecular formula C 6H 14. It is a branched hydrocarbon with a central carbon atom bonded to four other carbon atoms. The two methyl groups are attached to the central carbon, and the remaining two hydrogen atoms are attached to the terminal carbon atoms.The
connectivity and arrangement of carbon and hydrogen atoms in 2,2-dimethylbutane can be represented by the following structural formula:“` H H | |H
- C
- C
- C
- C
- H
| | H H“`
Hydrogen Atoms, Draw 2 2 dimethylbutane show all hydrogen atoms
- ,2-dimethylbutane contains a total of 14 hydrogen atoms. These hydrogen atoms can be classified into different types based on their position relative to the carbon atoms they are bonded to.
- *Primary hydrogen atoms are bonded to a carbon atom that is bonded to only one other carbon atom. There are six primary hydrogen atoms in 2,2-dimethylbutane.
- *Secondary hydrogen atoms are bonded to a carbon atom that is bonded to two other carbon atoms. There are four secondary hydrogen atoms in 2,2-dimethylbutane.
- *Tertiary hydrogen atoms are bonded to a carbon atom that is bonded to three other carbon atoms. There are four tertiary hydrogen atoms in 2,2-dimethylbutane.
Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of 2,2-dimethylbutane are determined by its structure and the presence of hydrogen atoms. 2,2-dimethylbutane is a relatively unreactive hydrocarbon due to the presence of the methyl groups, which hinder the approach of electrophilic reagents. However, it can undergo combustion, radical reactions, and substitution reactions under certain conditions.
FAQ Section: Draw 2 2 Dimethylbutane Show All Hydrogen Atoms
What is the molecular formula of 2,2-dimethylbutane?
C6H14
How many primary hydrogen atoms are in 2,2-dimethylbutane?
6
What is the IUPAC name of 2,2-dimethylbutane?
2,2-Dimethylbutane